
Trucos para dar sustos con el ESP32
Ahora que ya sabemos sonar canción de Halloween en ESP32, vamos a dar sustos con el ESP32 de la siguiente forma:
- Vamos a colocar nuestro circuito en una calabaza o en alguna decoración de Halloween.
- El circuito detectará cuando alguien se acerque y:
- Encenderá 2 leds (simulando los ojos).
- Emitimos un tono de música como vimos en el tutorial anterior.
Requerimientos:
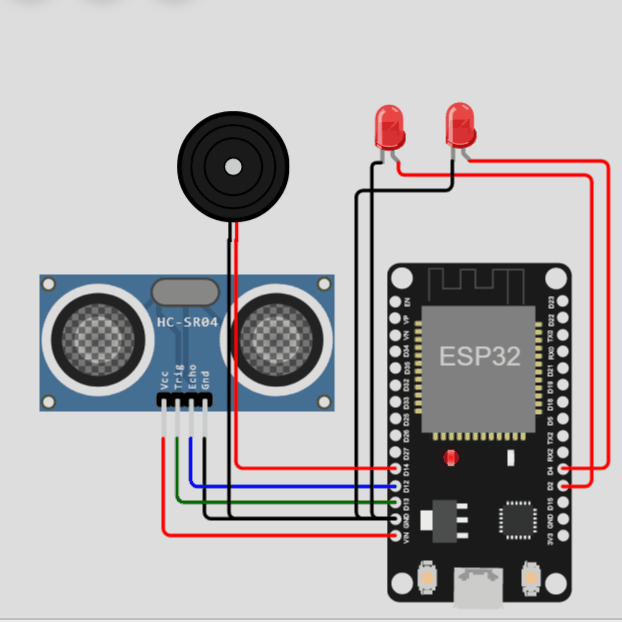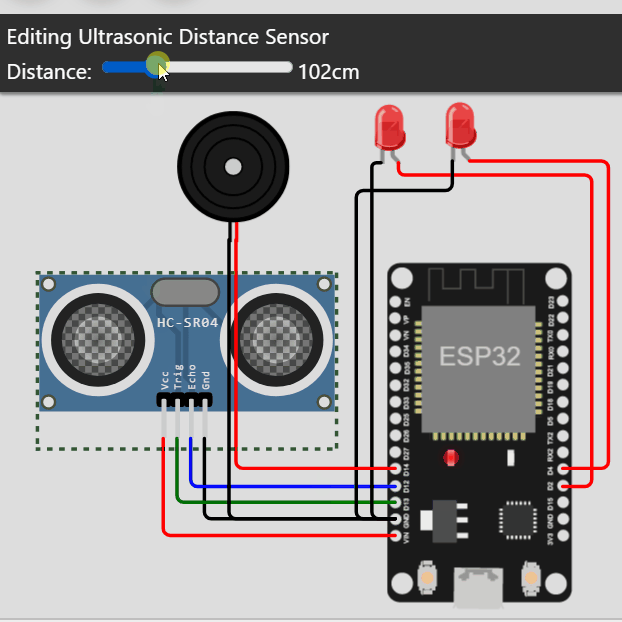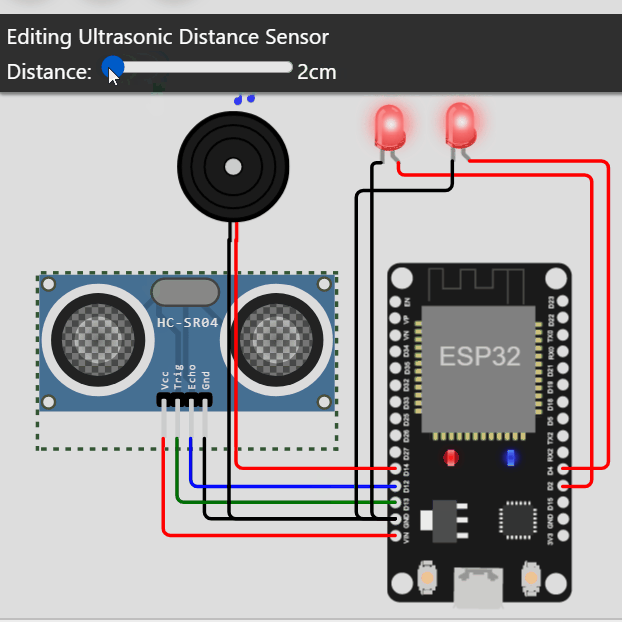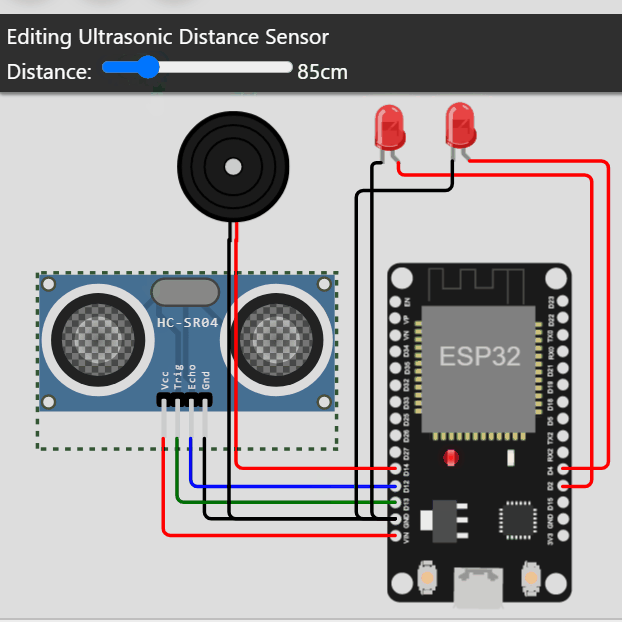
- ESP32.
- Zumbador.
- Sensor de Distancia.
- 2 Leds.
- Cables
Conexiones:
- Conectamos el Zumbador al pin 14.
- Conectamos el led1 al pin 2 y el led2 al pin4.
- Conectamos el Gatillo (Trig) al pin13 y el Echo al pin 12.
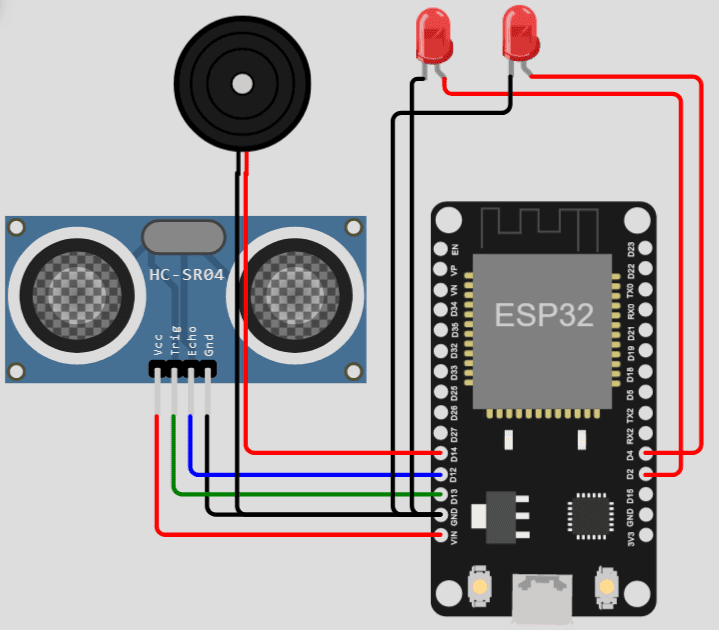
Código y diagrama: https://wokwi.com/projects/346036043311481426
Código de Sustos con el ESP32
/*
Sustos con el ESP32
*/
#define NOTE_B0 31
#define NOTE_C1 33
#define NOTE_CS1 35
#define NOTE_D1 37
#define NOTE_DS1 39
#define NOTE_E1 41
#define NOTE_F1 44
#define NOTE_FS1 46
#define NOTE_G1 49
#define NOTE_GS1 52
#define NOTE_A1 55
#define NOTE_AS1 58
#define NOTE_B1 62
#define NOTE_C2 65
#define NOTE_CS2 69
#define NOTE_D2 73
#define NOTE_DS2 78
#define NOTE_E2 82
#define NOTE_F2 87
#define NOTE_FS2 93
#define NOTE_G2 98
#define NOTE_GS2 104
#define NOTE_A2 110
#define NOTE_AS2 117
#define NOTE_B2 123
#define NOTE_C3 131
#define NOTE_CS3 139
#define NOTE_D3 147
#define NOTE_DS3 156
#define NOTE_E3 165
#define NOTE_F3 175
#define NOTE_FS3 185
#define NOTE_G3 196
#define NOTE_GS3 208
#define NOTE_A3 220
#define NOTE_AS3 233
#define NOTE_B3 247
#define NOTE_C4 262
#define NOTE_CS4 277
#define NOTE_D4 294
#define NOTE_DS4 311
#define NOTE_E4 330
#define NOTE_F4 349
#define NOTE_FS4 370
#define NOTE_G4 392
#define NOTE_GS4 415
#define NOTE_A4 440
#define NOTE_AS4 466
#define NOTE_B4 494
#define NOTE_C5 523
#define NOTE_CS5 554
#define NOTE_D5 587
#define NOTE_DS5 622
#define NOTE_E5 659
#define NOTE_F5 698
#define NOTE_FS5 740
#define NOTE_G5 784
#define NOTE_GS5 831
#define NOTE_A5 880
#define NOTE_AS5 932
#define NOTE_B5 988
#define NOTE_C6 1047
#define NOTE_CS6 1109
#define NOTE_D6 1175
#define NOTE_DS6 1245
#define NOTE_E6 1319
#define NOTE_F6 1397
#define NOTE_FS6 1480
#define NOTE_G6 1568
#define NOTE_GS6 1661
#define NOTE_A6 1760
#define NOTE_AS6 1865
#define NOTE_B6 1976
#define NOTE_C7 2093
#define NOTE_CS7 2217
#define NOTE_D7 2349
#define NOTE_DS7 2489
#define NOTE_E7 2637
#define NOTE_F7 2794
#define NOTE_FS7 2960
#define NOTE_G7 3136
#define NOTE_GS7 3322
#define NOTE_A7 3520
#define NOTE_AS7 3729
#define NOTE_B7 3951
#define NOTE_C8 4186
#define NOTE_CS8 4435
#define NOTE_D8 4699
#define NOTE_DS8 4978
//Declaramos el pin del zumbador
int pinZumbador=14;
int melodia[] = {
NOTE_CS5, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_CS5, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_CS5, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_D5, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_CS5, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_CS5, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_CS5, NOTE_FS4, NOTE_D5, NOTE_FS4
};
int duracionNotas[] = {
6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6
};
//Inicializamos las variables de la salida pwm
int canal=0, frec=2000, resolucion=8;
//Distancia del objeto
int distancia = 0;
//Pin del eco del sensor
int pinEco=12;
//Pin del gatillo del sensor
int pinGatillo=13;
//Pin que emite led
int pinLed1=2;
int pinLed2=4;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
//Inicializamos la salida del pwm
ledcSetup(canal,frec,resolucion);
//Declaramos pin donde se conecta el zumbador
ledcAttachPin(pinZumbador, 0);
//Inicializamos el pin donde se conectara el led
pinMode(pinLed1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinLed2, OUTPUT);
}
//Funcion que nos entrega la distancia
long readUltrasonicDistance(int triggerPin, int echoPin)
{
//Iniciamos el pin del emisor de reuido en salida
pinMode(triggerPin, OUTPUT);
//Apagamos el emisor de sonido
digitalWrite(triggerPin, LOW);
//Retrasamos la emision de sonido por 2 milesismas de segundo
delayMicroseconds(2);
// Comenzamos a emitir sonido
digitalWrite(triggerPin, HIGH);
//Retrasamos la emision de sonido por 2 milesismas de segundo
delayMicroseconds(10);
//Apagamos el emisor de sonido
digitalWrite(triggerPin, LOW);
//Comenzamos a escuchar el sonido
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
// Calculamos el tiempo que tardo en regresar el sonido
return pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
//Calculamos la distancia en cm
distancia = 0.01723 * readUltrasonicDistance(pinGatillo, pinEco);
//Mostramos la disstancia
Serial.println(distancia);
//Si la distancia es menor a 20 encendemos el led
if (distancia < 20) {
tonada();
}
//Si la distancia es mayor a 20 apagamos el led
else {
//Apagamos el sonido
ledcWriteTone(0, 0);
//Apagamos el led
digitalWrite(pinLed1, LOW);
digitalWrite(pinLed2, LOW);
}
//Apagamos el led
digitalWrite(pinLed1, LOW);
digitalWrite(pinLed2, LOW);
}
//Funcion que emite la tonada de halloween
void tonada(){
//Creamos un ciclo de 8 en 8
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
//Calculamos la duracion del tiempo de cada tonada
int duracionNota = 1000 / duracionNotas[i];
//emitimos la tonada almacenada previamente
ledcWriteTone(0, melodia[i]);
//Calculamos una paus entre tonadas
int pausaEntreTonadas = duracionNota * 1.30;
//Encendemos el led
digitalWrite(pinLed1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLed2, HIGH);
//Esperamos un tiempo
delay(pausaEntreTonadas);
//Apagamos el led
digitalWrite(pinLed1, LOW);
digitalWrite(pinLed2, LOW);
//Apagamos el sonido
ledcWriteTone(0, 0);
}
}
🎦 Este curso: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VuJkqL2Ys3Y&list=PLCTD_CpMeEKTvjzabAvLGHakg-ql6t0q6&ab_channel=ProgramadorNovato
🎦 Curso de Arduino: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oGinJt9aALc&list=PLCTD_CpMeEKSqw3Nh7rA9aXUAzbPIPkdv&ab_channel=ProgramadorNovato
🎦 [CURSO] C++ DE 0 A HEROE: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=APN8aCyPvww&list=PLCTD_CpMeEKTofxs7iottRxJ5YPM7BOc
